The Science of Stress: Understanding How It Affects the Mind and Body
Stress is an inevitable part of life. Whether it’s meeting deadlines at work, navigating personal challenges, or simply dealing with the fast pace of modern living, stress can feel like an ever-present force. But what exactly happens to our bodies and minds when we experience stress? And why can chronic stress contribute to mental health issues like anxiety, depression, and substance use?
Let’s dive into the science behind stress and explore how it affects us physically and mentally, along with practical tips to manage and reduce stress in your daily life.
What is Stress
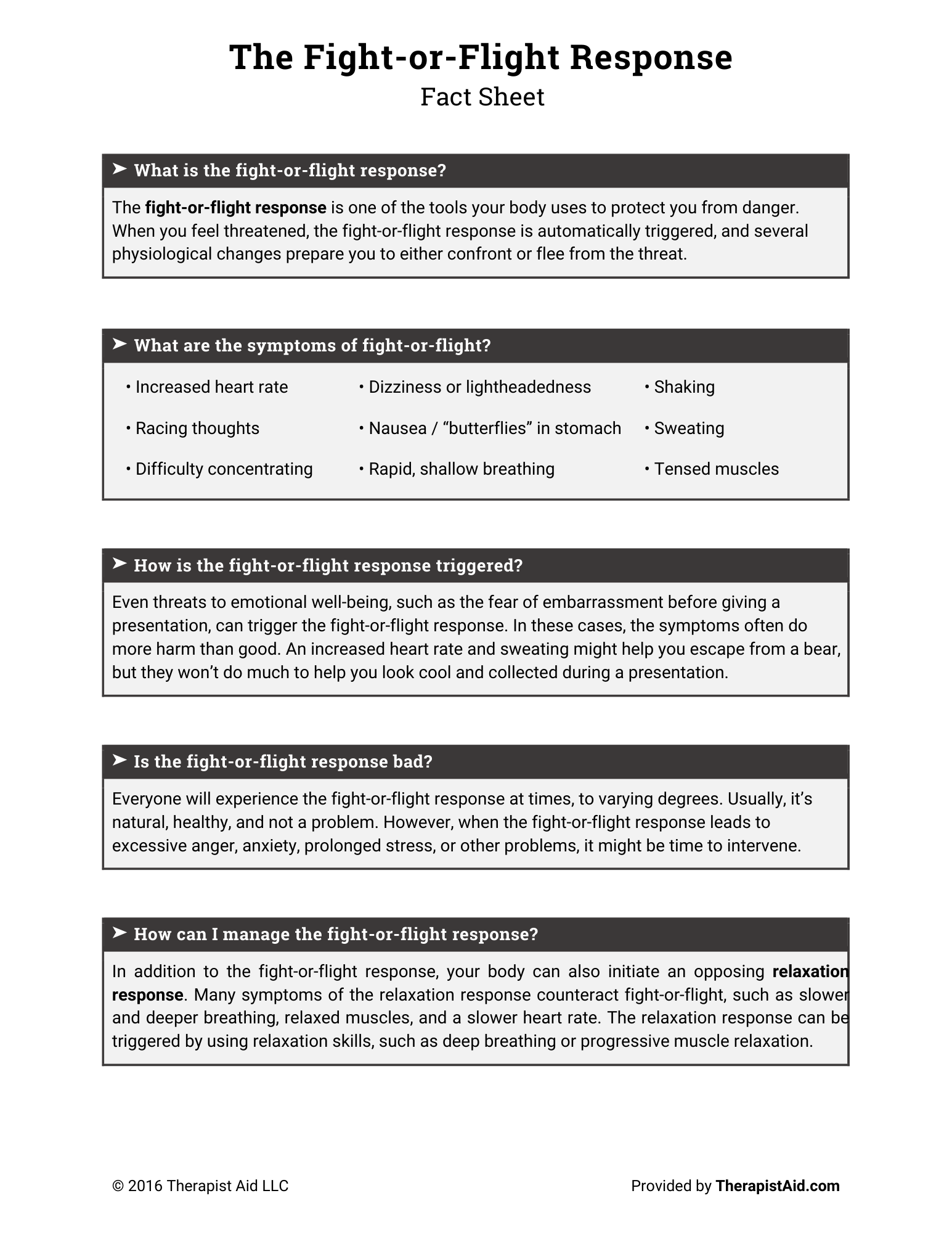
At its core, stress is the body’s natural response to a perceived threat or demand. This response is often referred to as the "fight or flight" mechanism. When we encounter a stressful situation, our body releases a cascade of hormones, including adrenaline and cortisol, that prepare us to either fight or flee from the threat.
In the short term, this response can be incredibly helpful. It boosts our energy, sharpens our focus, and prepares our body to take action. However, when stress becomes chronic—when it lingers for extended periods of time—it can start to have negative effects on both our body and mind.
How Stress Affects the Mind and Body
1. The Brain: When stress becomes chronic, it can interfere with the brain's normal functioning. Elevated cortisol levels can damage brain cells in areas responsible for memory and emotional regulation, such as the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. This can result in issues like memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and increased emotional reactivity.
Chronic stress can also disrupt the brain's ability to regulate emotions, leading to heightened anxiety, depression, and mood swings. Over time, this can contribute to the development of more severe mental health conditions.
2. The Body: The physical effects of chronic stress are also significant. Long-term stress can lead to a variety of health problems, including:
Cardiovascular Issues: Chronic stress increases blood pressure and heart rate, raising the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Immune System Suppression: Stress weakens the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to illnesses and infections.
Digestive Problems: Stress can affect the digestive system, leading to issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), heartburn, and nausea.
Sleep Disturbances: Stress is a common culprit behind sleep problems like insomnia, which can, in turn, exacerbate stress and mental health issues.
Substance Use: In an attempt to cope with chronic stress, some people may turn to substances like alcohol, drugs, or even overeating as a form of relief, which can lead to dependency and addiction.
3. Mental Health: Chronic stress doesn’t just impact our body—it takes a toll on our mental health as well. Persistent stress can lead to or worsen anxiety and depression. The constant pressure, worry, and fear associated with chronic stress can create a cycle of negative thinking, making it harder to break free and heal.
Over time, stress can become a trigger for more serious mental health issues, including panic attacks, burnout, and even post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in some cases.
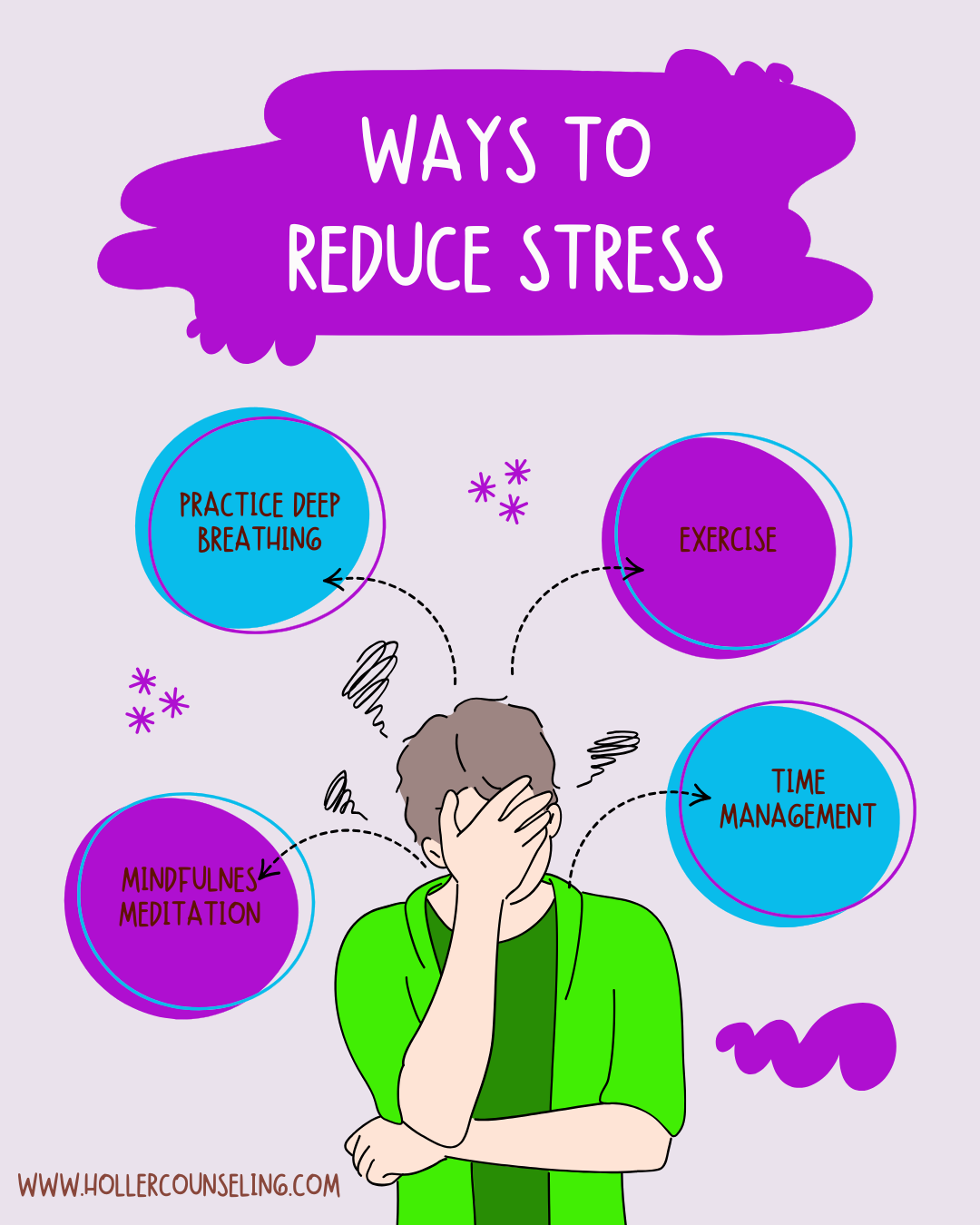
Tips for Managing Stress
The good news is that stress is manageable, and there are many strategies you can adopt to reduce its impact on your life. Here are some practical tips to help you cope with stress in a healthier way:
Relaxation Techniques:
Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR): This technique involves tensing and relaxing different muscle groups in the body. By doing so, you can release physical tension and promote a sense of calm.
Visualization: Close your eyes and imagine a peaceful, serene place, such as a beach or forest. Focus on the sights, sounds, and feelings associated with this place to help reduce stress and ground yourself.
Mindfulness Meditation: Mindfulness involves being fully present in the moment, without judgment. Regular mindfulness practice can help reduce stress and anxiety by allowing you to step away from the chaos and find inner peace.
2. Time Management: Effective time management is crucial for reducing stress, especially when life feels overwhelming. Here are a few tips:
Prioritize Tasks: Break down tasks into manageable chunks and prioritize them based on importance. Focus on completing one task at a time rather than multitasking.
Set Boundaries: Learn to say "no" when you’re already stretched thin. Setting boundaries helps protect your time and energy from unnecessary stressors.
Take Breaks: Don’t forget to take regular breaks during the day, especially if you’re working on a high-pressure project. A few minutes of relaxation or a short walk can help clear your mind and improve productivity.
3. Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing exercises are simple but incredibly effective for calming the nervous system and reducing stress.
One popular technique is diaphragmatic breathing:
Sit or lie down in a comfortable position.
Place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen.
Inhale deeply through your nose, ensuring that your abdomen rises (not your chest).
Exhale slowly and completely through your mouth.
Repeat for several minutes, focusing on the rhythm of your breath.
This practice can quickly help lower cortisol levels and bring your body into a more relaxed state.
4. Social Support: Connecting with others is essential for mental health. Reach out to family, friends, or a therapist to share your feelings. Social support can provide emotional comfort and remind you that you're not alone in your struggles.
5. Exercise: Physical activity is one of the best ways to combat stress. Exercise boosts the production of endorphins, which are chemicals in the brain that improve mood and promote relaxation. Whether it’s yoga, running, dancing, or walking, regular exercise helps reduce the physical tension caused by stress and improves overall well-being.


Conclusion/Final Thoughts
While stress is a normal part of life, chronic stress can have serious consequences for both our mental and physical health. Understanding the science of stress and how it affects the mind and body is the first step toward managing it effectively. By adopting stress management techniques like relaxation exercises, time management strategies, and breathing exercises, you can reduce the harmful effects of stress and promote a healthier, more balanced life.
If you find that stress is significantly impacting your life or contributing to anxiety, depression, or substance use, consider seeking professional help. A therapist or counselor can help you navigate your stressors and provide personalized strategies for managing your mental health.
Contact Counseling in the Holler, LLC today to set up an appointment or a free consultation to see if we’re the right fit for you. Your well-being is our priority, and we're here to support you every step of the way.