Mind-Body Connection: How Physical Health Impacts Mental Well-being
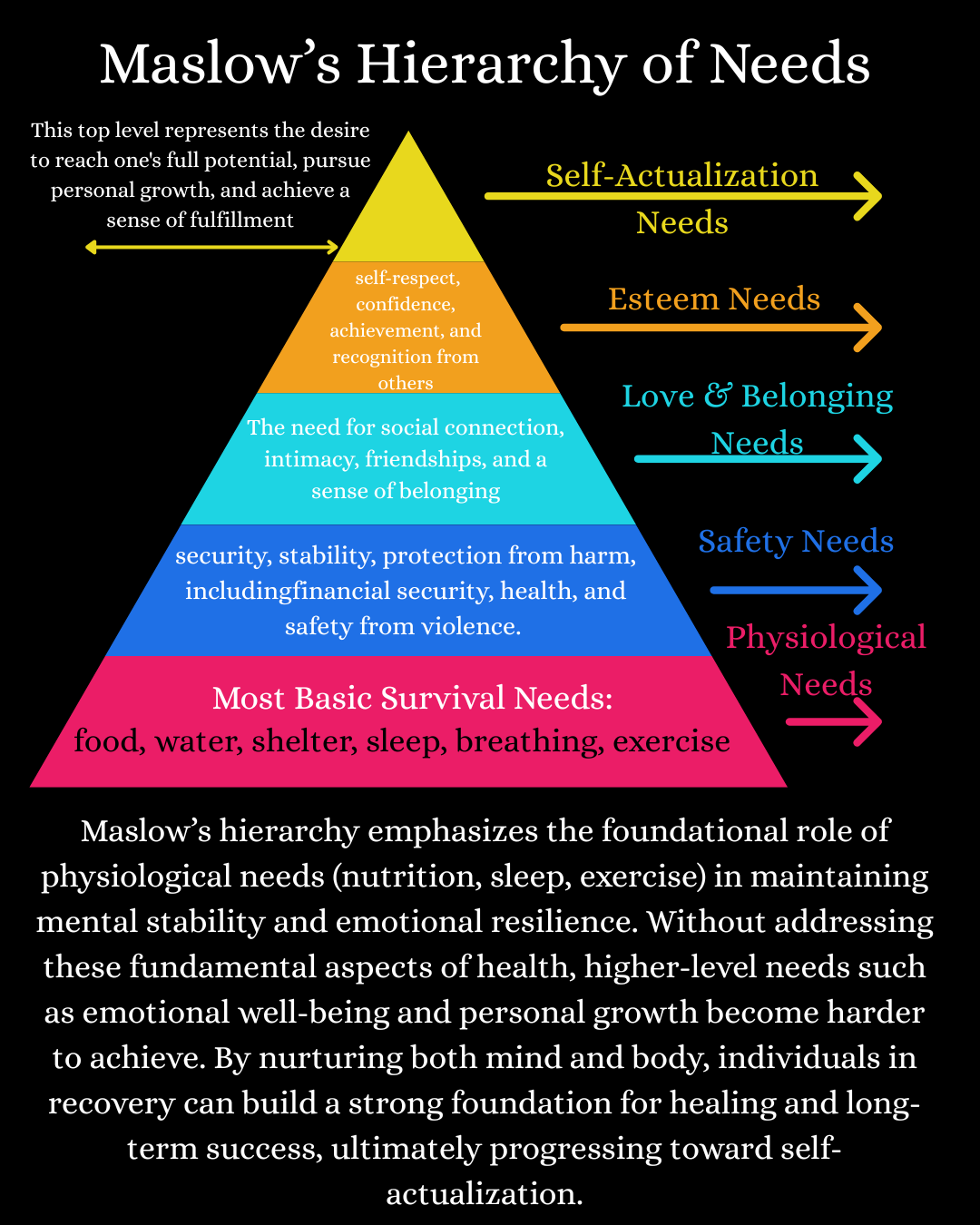
The mind-body connection is a powerful relationship that highlights how our physical health directly influences our mental wellness. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs emphasizes that our physiological needs—such as food, sleep, and physical well-being—form the foundation for higher levels of psychological growth and self-actualization. When these basic needs are met, individuals are better equipped to manage emotions, build resilience, and focus on personal growth. This is especially crucial for individuals in recovery, as stabilizing the body through regular exercise, proper nutrition, and good sleep hygiene provides the groundwork for emotional well-being and long-term healing. In this post, we’ll dive deeper into these areas, exploring the science behind them and how they contribute to a healthier mind and body.
Exercise: The Brain-Body Boost
Physical activity is one of the most powerful tools available for improving mental health. When we engage in exercise, our body produces endorphins—neurotransmitters that promote feelings of happiness and reduce the perception of pain. These "feel-good" hormones help alleviate stress, anxiety, and depression, while also increasing the production of other chemicals in the brain, like serotonin, which plays a crucial role in regulating mood, appetite, and sleep.
Research shows that exercise can be just as effective as antidepressant medications in treating mild to moderate depression. A study published in JAMA Psychiatry found that exercise significantly improved symptoms of depression, even in people who had no prior history of regular physical activity. The more intense and consistent the exercise, the greater the impact on mental health.
Harris, E. (2024). Meta-analysis: Exercise as effective as therapy for treating depression. JAMA, 331(11), 908. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2024.1121
For those in recovery, physical activity can provide a sense of accomplishment, control, and self-discipline. Whether it's running, yoga, swimming, or lifting weights, exercise offers a structured routine that can replace old, unhealthy habits. The act of sticking to a regular fitness regimen boosts self-esteem and reinforces the idea that positive change is possible.
Moreover, exercise can help reduce cravings and stress. A study from the American Journal of Preventive Medicine demonstrated that regular exercise can reduce alcohol cravings and the risk of relapse in people recovering from alcohol dependence. It acts as a natural stress reliever and provides an outlet for the emotional challenges of recovery, ultimately helping individuals build resilience and focus on their goals.
Brown, R. A., Abrantes, A. M., Read, J. P., Marcus, B. H., Jakicic, J., Strong, D. R., Oakley, J. R., Ramsey, S. E., Kahler, C. W., & Stuart, G. G. (2009). Aerobic exercise for alcohol recovery:
Rationale, program description, and preliminary findings. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 36(1), 49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2008.05.008
Nutrition: Fueling the Brain and Body
Our brains are highly energy-demanding organs, using up to 20% of the body’s daily energy intake. What we eat has a direct effect on our mental health and cognitive function. A well-balanced diet rich in whole foods, vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats can improve brain function, support emotional stability, and enhance recovery outcomes.
Nutrient-dense foods, such as leafy greens, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains, provide the building blocks necessary for healthy neurotransmitter function and brain cell regeneration. For example, omega-3 fatty acids—found in fatty fish like salmon, as well as plant-based sources like flaxseeds and walnuts—are crucial for cognitive health. Omega-3s have been linked to improved memory, mood regulation, and a reduced risk of mental health disorders like depression and anxiety.
For those in recovery, a nutrient-dense diet can play a vital role in stabilizing blood sugar levels and preventing energy crashes, which can lead to irritability and mood swings. Stabilizing blood sugar with complex carbohydrates—such as whole grains and vegetables—can prevent the rollercoaster of highs and lows often associated with processed foods and sugary snacks. This consistency helps maintain a balanced mood, especially when emotions run high during recovery.
Additionally, deficiencies in certain nutrients can have a significant impact on mental health. For instance, low levels of vitamin D have been linked to an increased risk of depression, and a deficiency in B vitamins can contribute to feelings of anxiety, fatigue, and poor concentration. Ensuring adequate intake of these essential nutrients through a balanced diet or supplementation can help improve overall mental wellness.
The role of nutrition in addiction recovery is particularly important. The brain's reward system becomes disrupted by substance use, often leading to poor dietary habits. By nourishing the body with wholesome foods, individuals can gradually restore balance to the brain's chemistry, supporting the healing process and preventing relapse.
Gómez-Pinilla, F. (2008). Brain foods: The effects of nutrients on brain function. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(7), 568–578. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2421
Sleep Hygiene: Recharging the Mind and Body
Sleep is one of the most critical components of both physical and mental health. A lack of quality sleep can impair cognitive function, increase emotional reactivity, and reduce the ability to handle stress. During sleep, the body and brain undergo essential restorative processes, including tissue repair, memory consolidation, and the removal of toxins that build up in the brain during wakefulness.
Sleep deprivation has been shown to affect mood, increase the risk of anxiety, depression, and irritability, and impair decision-making abilities. A study published in Sleep Medicine Reviews found that sleep problems are strongly associated with the development and exacerbation of mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and PTSD.
For individuals in recovery, sleep plays an even more crucial role. Poor sleep can make it harder to manage stress, increasing the likelihood of relapse. Conversely, quality sleep helps regulate emotional responses and enables individuals to approach recovery challenges with greater clarity and resilience. It’s during deep sleep stages that the brain consolidates learning and memories, both of which are vital for rebuilding a stable and positive mindset.
To improve sleep hygiene, individuals can establish a consistent bedtime routine. Creating a calm and relaxing environment—by dimming lights, avoiding screen time, and engaging in relaxation techniques like reading or meditation—can signal to the brain that it's time to unwind. Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, particularly in the hours leading up to bedtime, can also enhance sleep quality.
Sleep hygiene is also crucial for physical health. Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, weakened immunity, and weight gain, all of which can hinder the recovery process. A restorative night’s sleep helps the body heal and function optimally, supporting both the mental and physical aspects of recovery.
Freeman, D., Sheaves, B., Waite, F., Harvey, A. G., & Harrison, P. J. (2020). Sleep disturbance and psychiatric disorders. The Lancet Psychiatry, 7(7), 628–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30136-X


The Power of Balance: A Holistic Approach to Wellness
The integration of exercise, proper nutrition, and good sleep hygiene is a holistic approach that benefits both the mind and body. These factors work together to promote a stable, balanced mental state and support long-term recovery. When we nourish our bodies with exercise, nutrition, and rest, we create a foundation for resilience, emotional stability, and growth.
In recovery, these lifestyle changes not only help individuals heal physically, but they also foster a sense of empowerment and agency. By taking control of their health, individuals in recovery can experience increased self-esteem, a greater sense of accomplishment, and more sustainable success.
Ultimately, the mind-body connection is not just a metaphor—it’s a biological reality. The state of our bodies directly influences the state of our minds, and vice versa. By prioritizing physical health through exercise, nutrition, and sleep, we can create the conditions for optimal mental well-being, enhancing recovery and supporting overall life satisfaction.
By understanding and embracing the profound connection between mind and body, individuals can take meaningful steps toward achieving holistic health—an essential foundation for a fulfilling, balanced life.
For a deeper understanding of the mind-body connection and a personalized approach to your well-being, reach out to Counseling in the Holler, LLC. Schedule an appointment or a free consultation to see if we’re the right fit for you. Let us walk alongside you on your path to mental wellness and recovery.